The coverage range of a wireless link depends on the following factors:
- Transmit power
- Receiver Sensitivity
- Antenna gain
- Losses in the cables and various accessories (connectors, lightning surge protector)
- Loss in the air (variable depending on the frequency)
- Nature of objects to cross
For outdoor radio link installation, you will get a strong signal if the visibility is perfect (Clear Line of Sight) between the two antennas and if the Fresnel zone obstruction do not exceed 20%, see drawings below. Nevertheless in case of a partial or complete obstruction it may be possible to compensate the loss of signal with high gain directional antennas (for short distance and if obstacles are trees).
Generally, when the Fresnel zone is blocked with more than 20%, it will result in a reduced data rate and a risk of loss of communication intermittently.
Line of Sight (LOS)
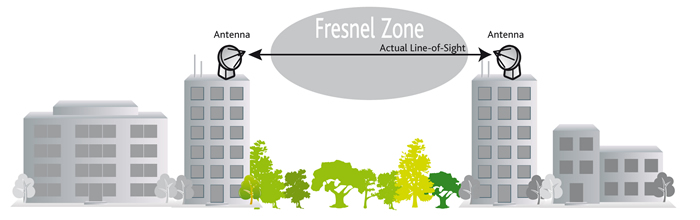
Near Line of Sight (near LOS)
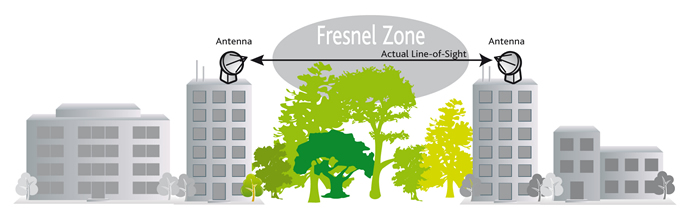
Non Line of Sight (NLOS)
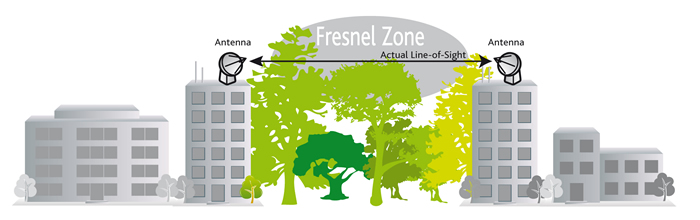
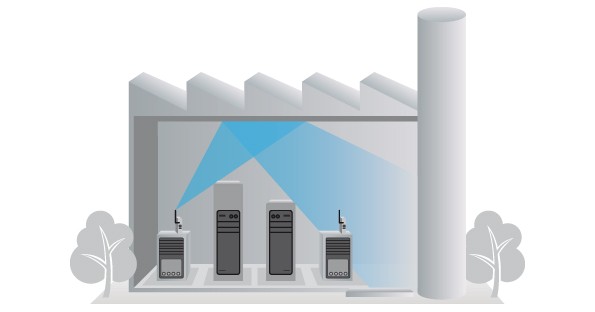
For an indoor radio link installation (factory, offices, warehouses …) the radio will operate quite well even if there is no line of sight between the antennas.
The quality of the connection will depend mainly on the nature of objects such as walls and partitions.
A standard office wall offers little resistance to the crossing of radio waves, however a concrete wall will block them almost totally.
The radio link quality in a warehouse or factory mainly depend on the diffracted and reflected waves by various objects (machines, walls, ceiling …), in this case it is strongly recommended to use equipments with two antennas that support the diversity mode, we offer several models that support the diversity mode.
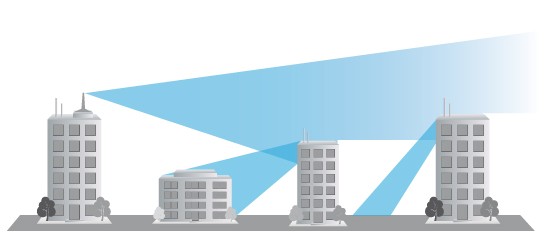
Reflected and diffracted waves can also be used to achieve radio coverage in urban areas even if there is no line of sight between the antennas, radio waves in this case are diffracted and reflected by buildings as shown below:
The losses in the air or when crossing objects depend on radio frequency, the higher the frequency is, the higher the losses will be significant. Loss in air at 5 GHz is twice as the loss at 2.4 GHz, the covered range will be divided by two. Here is a list of obstacles that can significantly affect the coverage range of a wireless link:
- Powerlines
- Existing WiFi networks
- Microwave
- Concrete walls
- Metal Shelters
- Trees
- Hills
- Buildings
- Metal Roofs
- Tinted glass or metallic glass
- Weather conditions (heavy rain)
- Earth radius curvature beyond 10 km
There are several tools that help in evaluating the coverage of a wireless radio network and also to calculate the angle and height of the antennas according to their characteristics. The four programs you can download below are Microsoft Excel files, click on the program you want to launch or to download:
| Radio link budget calculation tool | |
| Fresnel zone calculation tool | |
| Antenna downtilt coverage radius calculation tool | |
| Antennas downtilt calculation tool (according to the height) |



